How to resolve vulnerabilities in Front-End Applications
If you're working with front-end frameworks like React.js, Angular, or Vue.js, or if your project relies on a package.json file, you might encounter vulnerabilities when running npm audit or yarn audit. These vulnerabilities pose a security risk and need to be addressed promptly. This article will guide you through resolving vulnerabilities, particularly in React.js-based projects.
Understanding Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities refer to flaws or weaknesses in a software system that attackers can exploit to undermine the system's integrity, availability, or confidentiality. These can emerge from outdated packages, insecure configurations, or flawed code.
Resolving Vulnerabilities in Direct Dependencies
Direct dependencies (or devDependencies) are the packages that your project directly relies on. Here’s how you can address vulnerabilities in your React.js, Angular, or Vue.js applications:
-
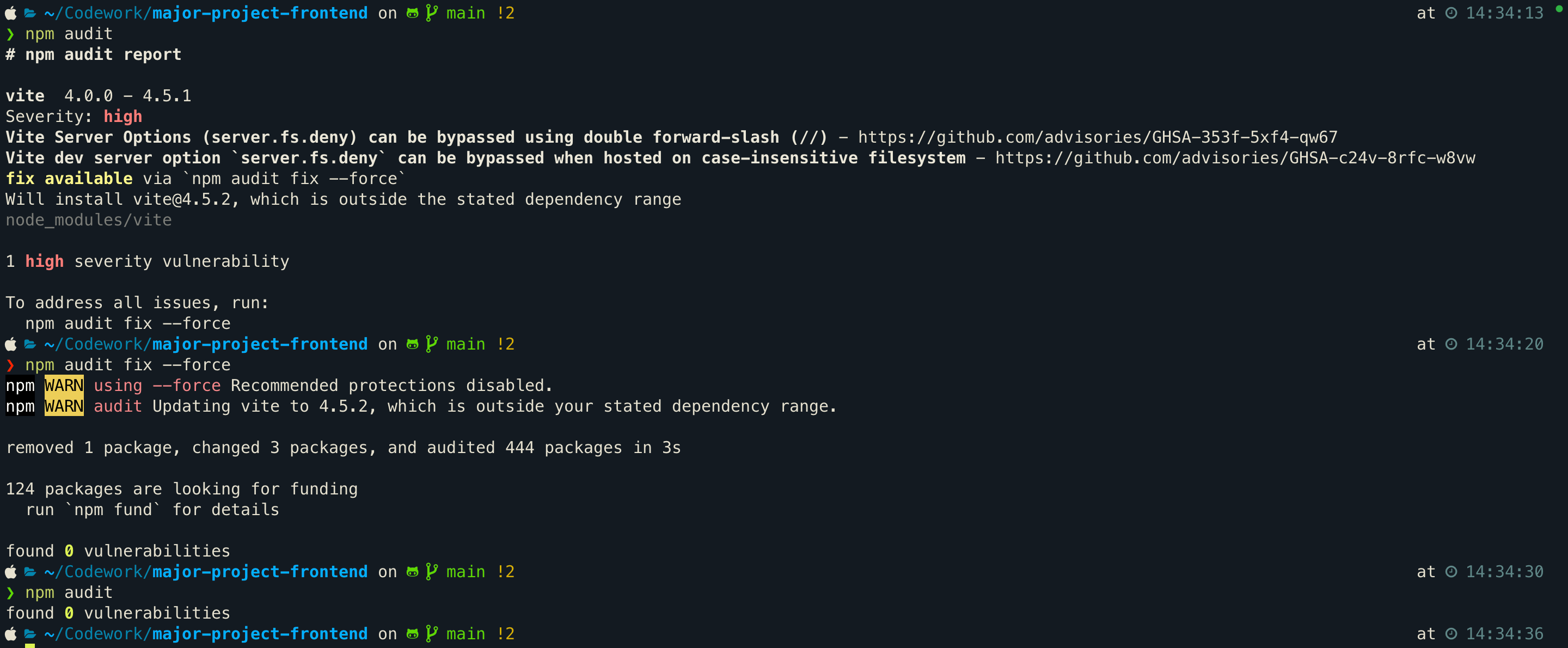
Identify Vulnerabilities: Execute
npm auditoryarn auditto uncover any vulnerabilities within your project. -
Assess Breaking Changes: Before updating any packages, verify whether there are breaking changes in the newer versions. Review the release notes of the packages or use
npm outdatedoryarn outdatedto identify any significant changes that could impact your application. -
Update Packages: After evaluating for breaking changes, rectify the vulnerabilities by executing
npm audit fixoryarn audit fix. This will typically upgrade the packages to the latest versions, thereby resolving the security issues. If you want to update a specific package, you can usenpm install package-name@latestoryarn add package-name@latest. Note: Avoid usingnpm audit fix --forceoryarn audit fix --forceas it can sometimes lead to downgrading packages, which might introduce new vulnerabilities. In such cases, it's better to manually update the packages by specifying the version in thepackage.jsonfile. -
Automate Security Checks: Incorporate vulnerability checks into your CI/CD pipeline by using
npm auditoryarn auditand configure the pipeline to fail if vulnerabilities are detected. Additionally, tools likenpm audit fixoryarn audit fixcan be employed to automatically correct vulnerabilities, streamlining the maintenance of your project's security.
 |
|---|
 |
|---|
Resolving Vulnerabilities in Indirect Dependencies
Vulnerabilities can also occur in indirect (or transitive) dependencies, which are packages that your direct dependencies require. These vulnerabilities need careful handling to avoid breaking your project. Here’s how to deal with vulnerabilities in indirect dependencies effectively:
-
Identify Indirect Vulnerabilities: Run
npm auditoryarn audit. These commands help in identifying both direct and indirect dependency vulnerabilities. -
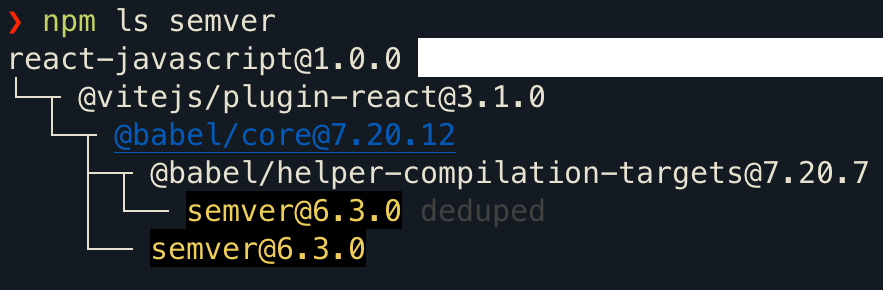
Analyze the Dependency Tree: Use
npm ls <package_name>oryarn list --pattern <package_name>to understand the dependency chain. This helps in pinpointing which direct dependencies are causing the indirect vulnerabilities. -
Update Direct Dependencies: Often, updating your project's direct dependencies can also update the indirect ones, resolving vulnerabilities. Follow the general update procedures as outlined in previous sections.
-
Manual Updates for Indirect Dependencies: If direct updates don't resolve the issues, you can manually update indirect dependencies in
Node.js v16.14.2 or laterandnpm v8.3.0 or later. Addoverridesfield in yourpackage.json:{
"overrides": {
"semver": "6.3.1"
}
}After specifying the override, run
npm installoryarn install. This modification forces all uses of the semver package to the specified version, potentially resolving the vulnerabilities. However, ensure compatibility as this may lead to issues if the updated version is incompatible with other dependencies. -
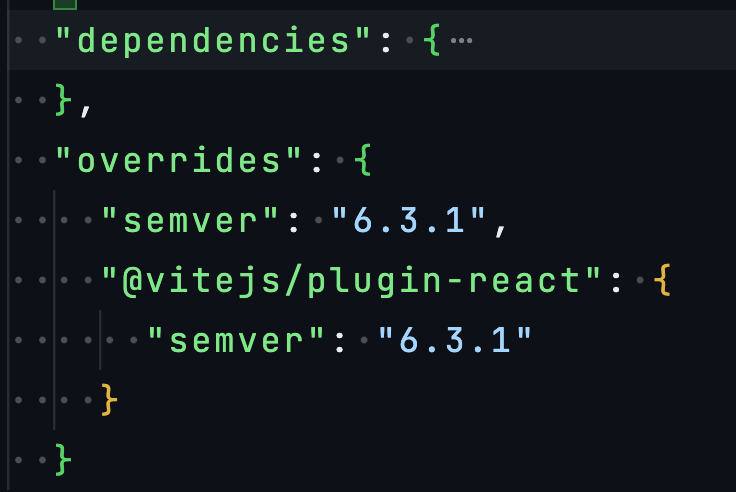
Specifying Overrides for Specific Packages: If you need to target a specific package for the update, you might add a more targeted override in your
package.json:{
"overrides": {
"@vitejs/plugin-react": {
"semver": "6.3.1"
}
}
}This ensures that only
@vitejs/plugin-reactuses the specified version ofsemver. Implement this, then runnpm installoryarn installto apply the changes. -
CI/CD Integration: Even if your CI/CD pipeline operates under
Node.js version 14, you can address vulnerabilities in indirect dependencies by leveraging theoverridesfeature. First, ensure that you haveNode.js version ^16.14.0locally. Then, add the necessary overrides to yourpackage.jsonand runnpm install. This process should generate an updatedpackage-lock.jsonfile reflecting the changes. In your CI/CD pipeline, utilize thepackage-lock.jsonfile from your local development environment to install dependencies. Execute the following command:
npm ci
This specific command ensures that your project installs dependencies exactly as defined in your package-lock.json, applying the overrides as intended and maintaining consistency across environments.
 |
|---|
 |
|---|
It's crucial to thoroughly test your application after making these changes to ensure everything works correctly and the vulnerabilities are resolved.
Best Practices for Security Maintenance
Enhance the security of your front-end applications with these straightforward practices:
-
Update Packages Regularly: Always use the latest versions of your packages to benefit from recent security updates. Consistent updates prevent compatibility issues and reduce security risks.
-
Automate Security: Implement automated security scans within your CI/CD pipeline. Early detection of vulnerabilities helps in their quick resolution, keeping your production environment secure.
-
Utilize Security Tools: Employ tools like
npm auditoryarn auditto find and address vulnerabilities. Tools such assnykornpm audit fixcan help automate the fixing process. -
Specify Exact Versions: When adding packages, use the
--save-exactflag withnpm installoryarn addto lock the versions. This prevents unintended updates and maintains consistency, reducing the likelihood of introducing vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Vulnerabilities in front-end applications represent considerable security threats. However, by adhering to the guidelines provided in this article, you can effectively mitigate these risks in your React.js, Angular, or Vue.js projects. Regular updates to your packages and the integration of automated security checks into your CI/CD processes are crucial steps in preserving the security and integrity of your applications. Stay proactive in your security practices to ensure a safer web environment for all users.
